History
History
1941: Acquisition of present site.1964: Completion of Second Building for studentfs experiment,
research and administration.
1966: Placement of the staffs (two educational staffs and
one administrative official)
1978: Completion of Building with light control system
for experimental research
2001: Establishment of FSC. The name was changed to Nanae Fresh-Water
Laboratory.
Propagation of Salvelinus species in Japan (Professor Tatsuro Kubo: 1966-83)

@In Japan, Salvelinus species, such as Salvelinus leucomaenis, and S. malma,
distributed upper part of rivers at lower temperature in Honshu Island.
In recent decades, the population size is decreasing and endangered.
In natural condition, these fish are cautious, while did not fit a person
with timidity under artificial condition. The first Director of this
station, Dr. Tasuro Kubo, collected the local population of S. leucomaenis,
from every part of Japan and tried to propagate these fish species.
At the beginning of his study, it was very difficult to propagate them,
because of their property of timidity and food preference. But, he
developed the procedures of propagation and had been getting progeny successively.
Now, some progeny remain in this station, as population of Honsyu-iwana.
Breeding and sex-control of fish by chromosome set manipulation (Associate Professor Hiroshi Onozato: 1983-1985)
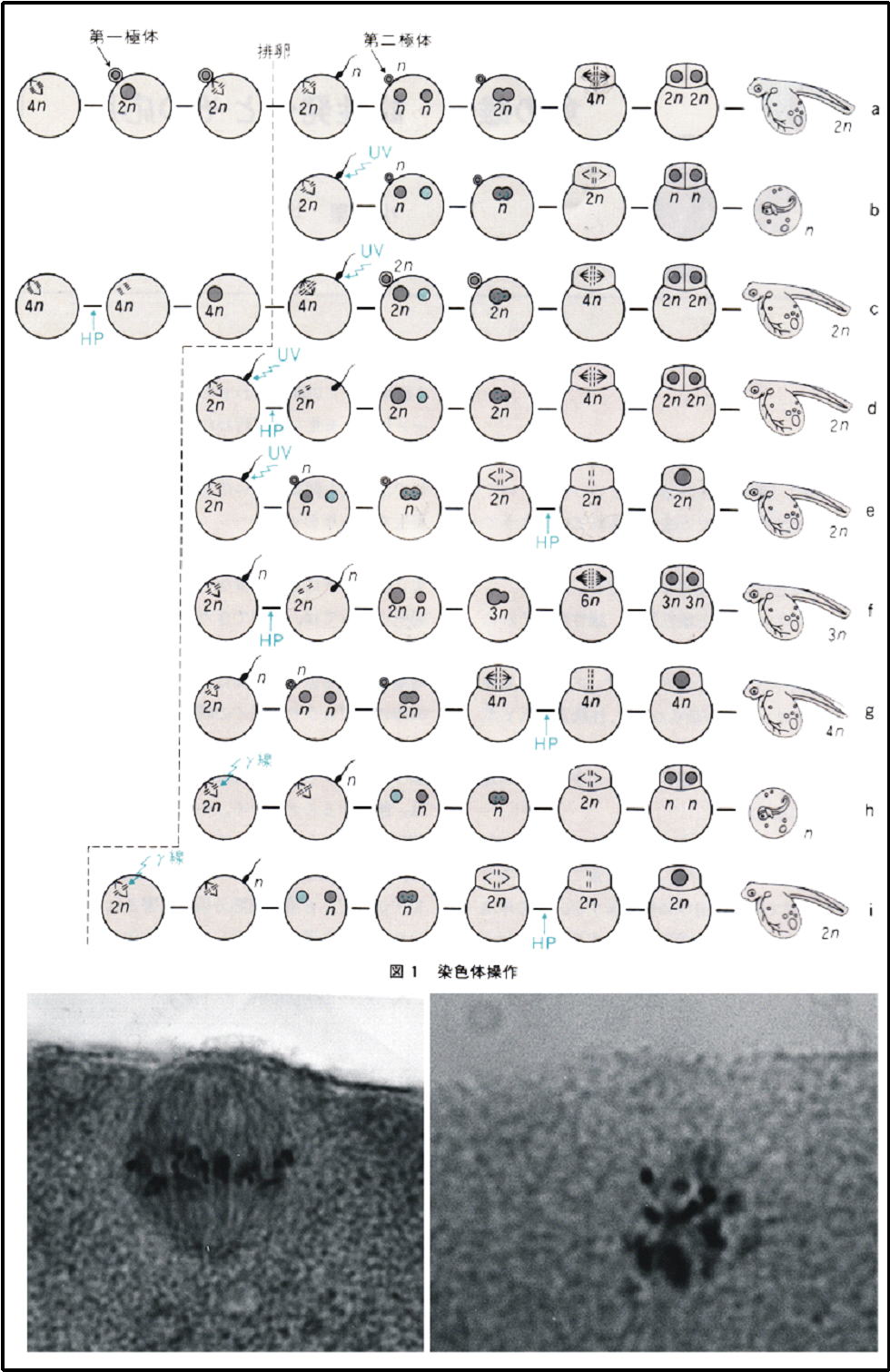
@In some case of commercial fish species, one of sexes has economically
higher value than the other. For example, female fish grow larger
than male in flatfish. In masu salmon, most female fish show sea-run
form and grow larger, while many male fish show resident in the river,
remaining small in size. Mono-sex aquaculture is useful in these
fish species. In XY sex determination system, artificial gynogenesis,
followed by inhibition of 2nd meiosis, induces all female population, while
artificial androgenesis, followed by inhibition of 1st cleavage division,
induces super-male individuals in half of descendants. In latter
case, all male population will be expected after fertilization between
XX female and YY super male. Also, inhibition of 2nd meiosis
and inhibition of 1st cleavage after normal fertilization are expected
to induce triploid and tetraploid individuals in descendants, respectively.
Associate Professor Hiroshi Onozato, who was the second director of the
Nanae Fresh-Water Station, developed the procedures of the chromosome set
manipulation in Salmonid species and actually induced all female population.
He moved to the National Institute of Aquaculture in 1985.
Immunobiochemical studies in teleost fish@(Associate Professor Akihiko Hara: 1986-1998)
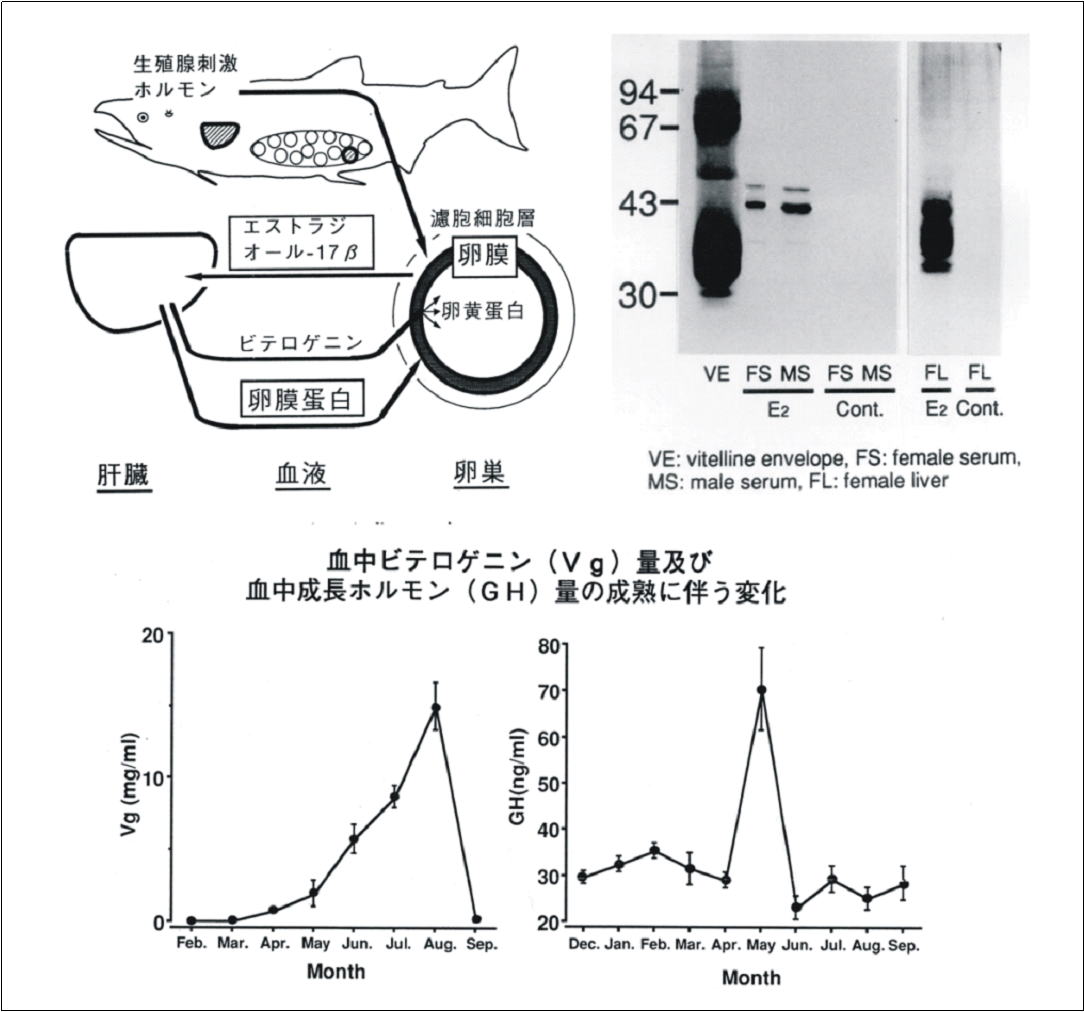
@During oogenesis, several kinds of proteins of egg yolk are bio-synthesized in liver and moved to ovary through blood. In the case of male without oocyte, these proteins are not synthesized. Therefore, analysis of blood proteins reveals the timing of egg differentiation and the sex of each individual. Using this concept, Associate Professor Akihiko Hara, who was the third director of the Nanae Laboratory, had conducted the immunobiochemical studies in teleost species. Fore example, he and his collaborators revealed that the egg differentiation in Ito Hucho perryi, whose first maturation is 6 year old, starts at 4 years old. However, it was revealed that male occasionally bio-synthesized the egg protein against expectation. During the following study, it has been revealed that the occasional serum yolk proteins had been induced by environmental hormonal substances distributed naturally. Thereafter, detection methods of these kinds of substances had been established. Dr. Hara collected many salmonid spcecies all over the world for his study. He moved to Faculty of Fisheries, Hokkaido University, as Professor, in 1998.
Breeding and development of aquaculture apparatus@(Chief Technical Officer Mr. Sizuo Kimura: 1970-2013)
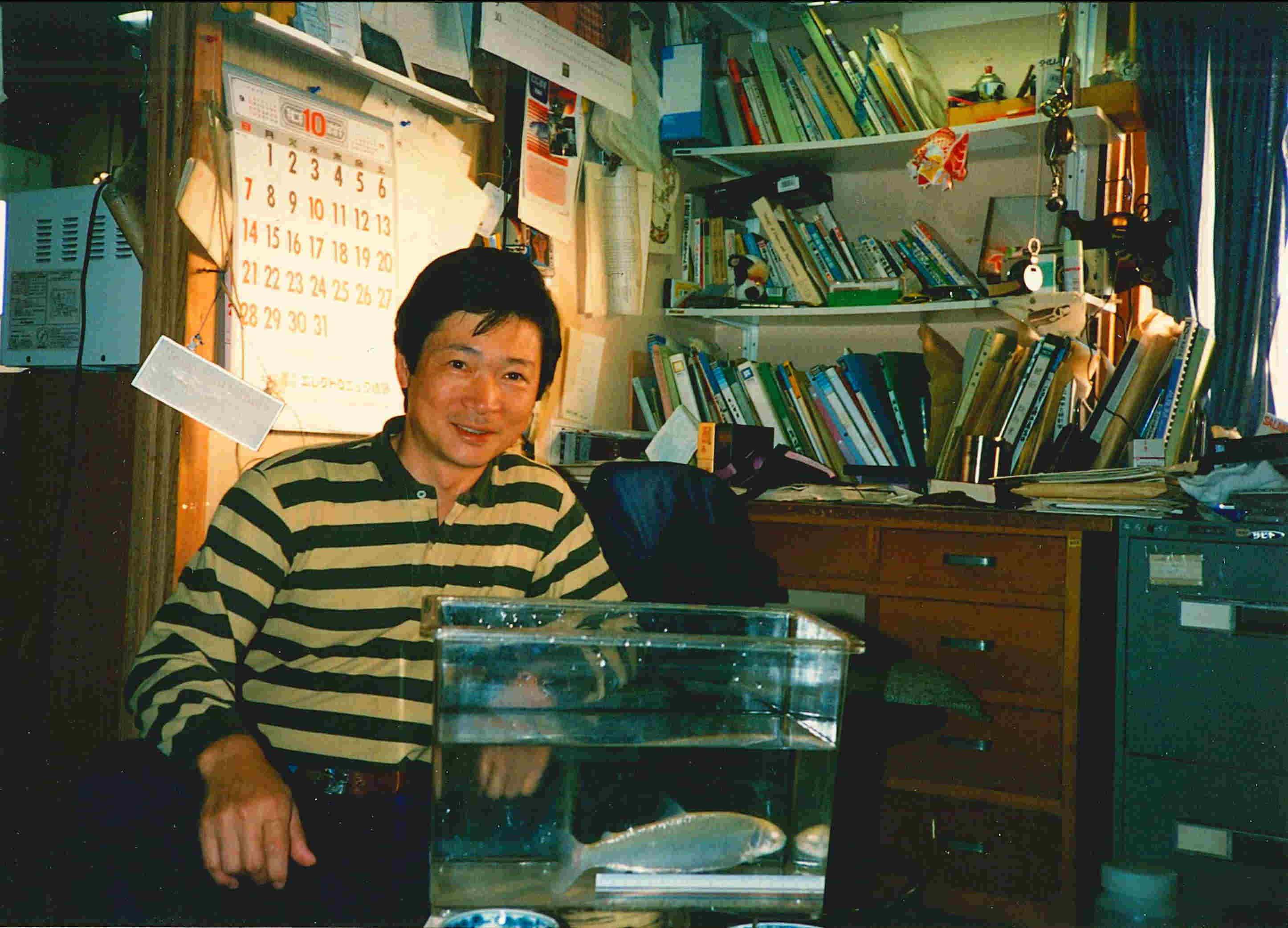

@Many kinds of aquaculture apparatus, such as Multi-High-Dense Aquariums, have been developed by Chief Technical Officer Mr. Sizuo Kimura. Hucho perryi. (Japanese name Ito), is the largest fresh-water fish distributed in Hokkaido, and now endangered. Mr. Kimura has been studying and established propagation techniques of this fish. He transferred his techniques to Ajigasawa Fishery Cooperatives, in Aomori Prefecture. During his work, he found five albino embryos from Sorachi strain of this fish in 1989. He carefully cultivated these albino individuals and established albino strain 11 years after finding. In masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou, he bred new strain without black spot. Black spots are not integrated by simple Mendelian inheritance. They may be integrated by poly-genes, because individuals with black spot are find even after five generations. He retired in 2013 spring, remaining many legends
oi[Xy[X
Nanae Fresh-Water Station
2-9-1, Sakuracho, Nanae town Kameda-gun, Hokkaido, 041-1105, Japan
TEL 0138-65-2344
FAX 0138-65-2239